Racemic and conglomerate 1-(4-haloaryl)ethylammonium tetrachlorocobaltate salts: formation of helical structures†
Abstract
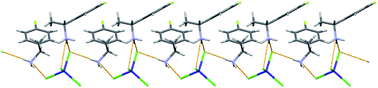
The racemic ligand rac-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethylamine (rac-fpea) reacts with cobalt(II) chloride in the presence of hydrochloric acid forming an A2CoCl4 type salt, [rac-fpeaH]2[CoCl4] (1). The salt crystallizes in the centro-symmetric P![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) space group. In contrast, under identical conditions the chloro derivative rac-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylamine (rac-cpea) yields a conglomerate of A3CoCl4Cl type salts, namely, [(R)-cpeaH]3[CoCl4]Cl (2R) and [(S)-cpeaH]3[CoCl4]Cl (2S), which crystallize in the chiral space group P21. Single crystal X-ray diffraction data for the crystals reveal nearly identical unit cells but different chirality. The two enantiomers crystallize out together and do not form separate colonies and exhibit similar morphology and color. In order to ascertain the assignment of chiral structures to the conglomerate crystals, the two salts are also independently synthesized from enantiomerically pure R-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylamine. We propose that the weak Cl⋯N interaction found in the structures may be involved in the conglomerate formation from rac-cpea. In addition, the analogous salt from R-(+)1-(phenyl)ethylamine, [(R)-peaH]3[CoCl4]Cl (3R), is also synthesized and characterized. The packing of the chiral cations and [CoCl4]2− anions in the crystals of 1, 2R, 2S and 3R are characterized by helices formed through inter-ionic H-bonding interactions. Thermogravimetric data measured in the range of 25–650 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere reveal that the compounds are stable up to T < 170 °C.
space group. In contrast, under identical conditions the chloro derivative rac-1-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylamine (rac-cpea) yields a conglomerate of A3CoCl4Cl type salts, namely, [(R)-cpeaH]3[CoCl4]Cl (2R) and [(S)-cpeaH]3[CoCl4]Cl (2S), which crystallize in the chiral space group P21. Single crystal X-ray diffraction data for the crystals reveal nearly identical unit cells but different chirality. The two enantiomers crystallize out together and do not form separate colonies and exhibit similar morphology and color. In order to ascertain the assignment of chiral structures to the conglomerate crystals, the two salts are also independently synthesized from enantiomerically pure R-(4-chlorophenyl)ethylamine. We propose that the weak Cl⋯N interaction found in the structures may be involved in the conglomerate formation from rac-cpea. In addition, the analogous salt from R-(+)1-(phenyl)ethylamine, [(R)-peaH]3[CoCl4]Cl (3R), is also synthesized and characterized. The packing of the chiral cations and [CoCl4]2− anions in the crystals of 1, 2R, 2S and 3R are characterized by helices formed through inter-ionic H-bonding interactions. Thermogravimetric data measured in the range of 25–650 °C under a nitrogen atmosphere reveal that the compounds are stable up to T < 170 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...