Binding mechanism of nine N-phenylpiperazine derivatives and α1A-adrenoceptor using site-directed molecular docking and high performance affinity chromatography†
Abstract
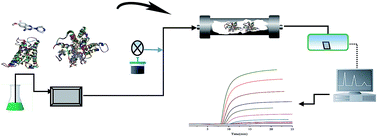
N-Phenylpiperazine derivatives are widely used as clinical drugs for fighting diseases related to the cardiovascular system by mediating the signal pathway of α1-adrenoceptor. The binding mechanism of nine N-phenylpiperazine derivatives to α1A-adrenoceptor was explored using molecular docking and high performance affinity chromatography. The methodology involved homology modelling of the three dimensional structure of α1A-adrenoceptor, predication of the binding behaviors using LIBDOCK and investigation of the thermodynamic behaviors of the binding by frontal analysis. Molecular docking results showed that Asp106, Gln177, Ser188, Ser192 and Phe193 of the receptor were the main binding sites for the nine N-phenylpiperazine derivatives binding to α1A-adrenoceptor. The binding was driven by formation of hydrogen bonds and electrostatic forces. The affinity of these derivatives for the receptor depended on the functional groups of an ionizable piperazine, hydrogen bond acceptor and hydrophobic moiety in the ligand structures. Frontal analysis indicated that the association constants of these compounds for the receptor were determined by their structural deviations in the above-mentioned functional groups. Thermodynamic studies presented negative enthalpy and Gibbs free energy changes with a positive entropy change, providing proof that the binding of the derivatives to α1A-adrenoceptor was mainly driven by electrostatic forces. This result was in line with the binding mechanism predicted by molecular docking. It is possible to explore the binding mechanism of drug candidates specifically binding to α1A-adrenoceptor using receptor chromatography.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...