Novel application of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose to improving direct compaction properties of tablet fillers by co-spray drying
Abstract
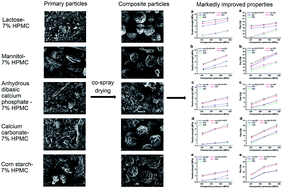
This work aimed to investigate the novel application of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) to improving the direct compaction properties of tablet fillers by co-spray drying. Three commonly used types of fillers were investigated. Two representatives were chosen for each type, i.e., (i) water-soluble small molecules: lactose and mannitol; (ii) water-insoluble small molecules: calcium carbonate and anhydrous dibasic calcium phosphate; and (iii) macromolecules: corn starch (practically insoluble in cold water) and chitosan (sparingly soluble in water). Except for chitosan, improvements on both powder properties (e.g., flowability and hygroscopicity) and tableting properties (e.g., tableting ratio, yield pressure, tensile strength, and Esp) were achieved for the rest five fillers by co-spray drying with a small amount of HPMC. This is mainly attributed to the homogeneous distribution of plastic and nonhygroscopic HPMC macromolecules on the surface of the primary and composite particles. In addition, changes induced by spray drying, such as agglomeration, spheroidization, porosity increase, amorphous formation, and gelatinization, also contribute to some degree to the improvements. The above results, together with the data of lubrication sensitivity and tablet disintegration, show that such a novel application of HPMC is effective and promising.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...