‘Aggregation induced phosphorescence’ active iridium(iii) complexes for integrated sensing and inhibition of bacterial growth in aqueous solution
Abstract
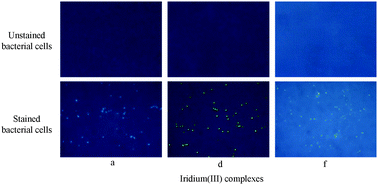
The present study attempts to develop a sensitive method to utilize ‘aggregation induced phosphorescence (AIP)’ active iridium(III) complexes as potential agents for “integrated” sensing and inhibition of bacterial growth in aqueous systems. The utilization of iridium(III) complexes for microbial detection in bodies of water has been demonstrated using Escherichia coli (E. coli) as a representative bacterial strain. The tested iridium(III) complexes also exhibited antibacterial properties against representative Gram positive and Gram negative bacterial strains with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 4 and 8 μg mL−1, respectively. Microscopic observations indicated that these complexes could penetrate into the bacterial cells and result in subsequent cell death. Preliminary mechanistic studies showed that the DNA binding ability of the iridium(III) complexes is responsible for their antibacterial properties. The observed “dual” role in detection as well as inhibition of bacterial growth makes this study highly promising and encouraging for the exploration of the applicability of other less expensive metal complexes for monitoring and controlling the bacterial levels in drinking and sea water systems at a commercial level.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...