Tumor specific delivery with redox-triggered mesoporous silica nanoparticles inducing neovascularization suppression and vascular normalization
Abstract
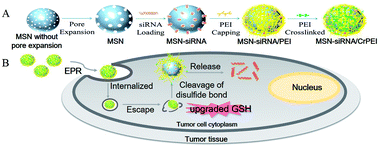
RNA interference (RNAi) has great potential in cancer therapy, however, efficient cytoplasmic delivery still remains a major challenge. In this study, redox-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles with enlarged pores (denoted as MSN-siRNA/CrPEI) were designed by immobilizing polyethylenimine (PEI) via intermediate linkers of disulfide bonds onto the MSNs as caps for redox-responsive intracellular gene delivery. The MSN-siRNA/CrPEI with a high siRNA loading capacity (35 mg siRNA per g MSNs) could react to the specific reductive stimulation—upgraded glutathione concentration in tumor cells and release cargos through the rupture of disulfide bonds. Subsequently, MSN-siRNA/CrPEI was used to deliver VEGF siRNA for cancer therapy and the underlying mechanisms were explored. As we expected, MSN-siRNA/CrPEI could be readily internalized into cells, escaped from the endolysosomes and was distributed in the cytoplasm where siRNA mediated its function. MSN-siRNA/CrPEI showed remarkable anti-tumor efficacy by the suppression of neovascularization and vascular normalization after peritumoral application against mice with KB tumors, proved by interstitial fluid pressure (IFP) reduction, CD31 suppression and angioplerosis. Notably, siRNA combined with dexamethasone exerted a better treatment effect which is attributed to the strong capability of dexamethasone to decrease the IFP, and a lower IFP leads to an improvement in the delivery and efficacy of exogenously administered therapeutics. These results indicate that the tumor specific delivery of siRNA with redox-triggered mesoporous silica nanoparticles is a promising strategy to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Neovascularization suppression and vascular normalization may be beneficial for cancer inhibition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...