α-Lipoic acid protects HAECs from high glucose-induced apoptosis via decreased oxidative stress, ER stress and mitochondrial injury
Abstract
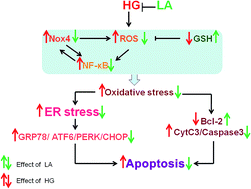
α-Lipoic acid (LA) has a wide range of benefits in treating diabetes mellitus (DM) and DM vascular diseases, however, the specific mechanisms are not clearly understood. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether LA confers a cytoprotective effect on human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) in the presence of high glucose concentration and the possible mechanisms involved in this effect. The apoptotic cells were detected by Annexin-V/PI and DAPI staining. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) were measured by flow cytometry assay. The change of mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔΨm) was analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscope. The expressions of NADPH oxidase 4 (Nox4), p22phox and Bcl-2 were measured by qRT-PCR and western blot analyses. Cytochrome C release from mitochondria, caspase-3 expression, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) were evaluated by western blot analyses. The results showed that LA inhibited endothelial cell apoptosis and decreased apoptosis related proteins expression. LA reduced ROS generation and over-expression levels of Nox4, p22phox induced by high glucose. LA also suppressed ER stress and the decreasing of ΔΨm as well as the activation of NF-κB. These results indicated the preventive effects of LA on HAECs apoptosis caused by high glucose and the effects might be obtained via inhibition of Nox4. These findings provide a new interpretation on the role of LA in the treatment of diabetes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...