Role of multivalent Cu, oxygen vacancies and CuO nanophase in the ferromagnetic properties of ZnO:Cu thin films
Abstract
Comprehensive microstructural, electronic and magnetic analyses have been carried out on ZnO:Cu thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition on c-plane sapphire under different oxygen partial pressures. Detailed X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) analyses reveal that increase in oxygen growth pressure degrades the epitaxy of ZnO:Cu thin films due to inclusion of nanosize CuO in the ZnO host lattice. HRTEM and magnetization studies suggest that thin film quality plays a less effective role in governing the magnetic properties of these samples. Instead, room temperature ferromagnetism (FM) of these ZnO:Cu thin film samples are highly tunable by the simultaneous presence of CuO nanophases and multivalent Cu and 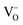 concentrations, which are in strong contest with each other. For low oxygen partial pressure grown sample, the effective
concentrations, which are in strong contest with each other. For low oxygen partial pressure grown sample, the effective 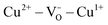 network is the main contributor to the observed FM and is in competition with CuO nanophases only when there is a relatively low
network is the main contributor to the observed FM and is in competition with CuO nanophases only when there is a relatively low 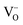 concentration with a dominant Cu2+ oxidation state. For vacuum grown samples containing high
concentration with a dominant Cu2+ oxidation state. For vacuum grown samples containing high 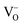 concentration and Cu1+ as dominant oxidation state, the
concentration and Cu1+ as dominant oxidation state, the 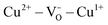 network becomes less effective and a CuO nanophase (4–5 nm) is the dominent FM supplier. The extrinsic FM in the vacuum grown sample, which is the best epitaxial quality sample, is further confirmed by the zero field cooled (ZFC) and field cooled (FC) magnetization protocols.
network becomes less effective and a CuO nanophase (4–5 nm) is the dominent FM supplier. The extrinsic FM in the vacuum grown sample, which is the best epitaxial quality sample, is further confirmed by the zero field cooled (ZFC) and field cooled (FC) magnetization protocols.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...