Effects of tetracycline on simultaneous biological wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removal†
Abstract
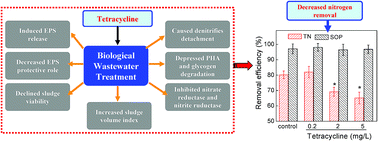
The impact of tetracycline on simultaneous biological wastewater nitrogen and phosphorus removal and its fundamental mechanisms were investigated in this study. Compared with the control, a lower concentration of tetracycline (0.2 mg L−1) did not exert adverse effects on biological nutrient removal; however, the presence of 2 and 5 mg L−1 of tetracycline decreased the total nitrogen removal efficiency from 80.2% to 69.2% and 65.1% respectively, but they showed marginal influence on phosphorus removal. The mechanism studies showed that most of the influent tetracycline was adsorbed by sludge, which induced the release of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from a sludge matrix, decreased the protective role of EPS on bacterial cells, declined the viability of sludge, increased the sludge volume index, and caused the detachment of denitrifying bacteria from sludge. Thus, the denitrifiers were more easily contacted with tetracycline. Further investigation revealed that it was the denitrifiers instead of nitrifiers being negatively affected by tetracycline, and the generation of electron donor for denitrification via intracellular polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) decomposition was depressed. In addition, tetracycline inhibited the activities of nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase as it was a strong chelating agent which reduced the free copper ions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...