Efficient amine functionalization of graphene oxide through the Bucherer reaction: an extraordinary metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction
Abstract
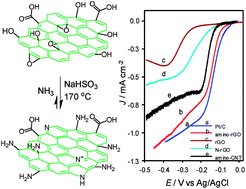
A simple and reliable method based on the Bucherer reaction is proposed for the functionalization of graphene oxide (GO) with amine (–NH2) groups. In the proposed method the chemical reaction between ammonia and GO, as precursor materials, is catalyzed with sodium bisulfite. The prepared amino-reduced graphene oxide (amino-rGO) was characterized with spectroscopic and imaging techniques including FTIR, XRD, XPS, SEM, EDX elemental mapping and thermal-gravimetric analysis (TGA). The surface analysis and material characterization reveal the high percentage of amine functional groups that can be achieved via this method. The investigation of the electrocatalytic activity of the prepared amino-rGO toward the oxygen reduction reaction confirms the significant improvement in the catalytic activity of amine functionalized graphene surface in the vicinity of doped nitrogen in the same graphene framework. The onset potential of ORR vs. Ag/AgCl in a 0.1 M KOH solution is observed at −0.07 V and the peak current density is 1.15 mA cm−2 comparable to the observed values for Pt/C as an electrocatalyst (onset potential −0.04 and peak current density 1.17 mA cm−2). This prepared amino-rGO is important to future research for the extension of various graphene-based composites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...