Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of magnetically separable γ-Fe2O3/N,Fe codoped TiO2 heterojunction for degradation of Reactive Blue 4 dye
Abstract
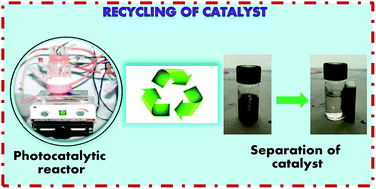
In the present work, nanocrystalline undoped, N-doped and N,Fe codoped TiO2 have been synthesized using a sol–gel method for the photocatalytic degradation of Reactive Blue 4 dye under visible light, with N,Fe codoped TiO2 exhibiting the best activity. Furthermore, to counter the problem of separation of the N,Fe codoped TiO2 photocatalyst, magnetically separable γ-Fe2O3/N,Fe codoped TiO2 heterojunctions were fabricated and found to exhibit enhanced photoactivity with 100% dye degradation, compared to 85% with N,Fe codoped TiO2. This behavior has been attributed to the facilitated electron–hole transfer in the γ-Fe2O3/N,Fe codoped TiO2 heterojunctions, low electron–hole recombination rate, existence of a pure anatase phase and narrow band gap of 1.5 eV. The recycled γ-Fe2O3/N,Fe codoped TiO2 also demonstrated good repeatability of photoactivity. The mechanism involved in the degradation of dye by γ-Fe2O3/N,Fe codoped TiO2 has also been discussed. In conclusion, the synthesis of magnetically separable and visible light active titania by the coupling of γ-Fe2O3 and N,Fe codoped TiO2 to overcome the limitations of a narrow band gap and non-recyclability, with the additional advantage of enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of Reactive Blue 4 dye, has been achieved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...