Recent progress in the development of sortase A inhibitors as novel anti-bacterial virulence agents
Abstract
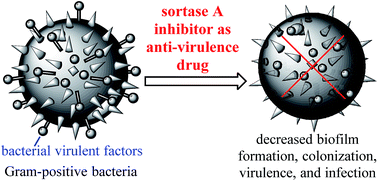
Sortase A (SrtA) is a membrane-associated enzyme responsible for the covalent anchoring of many virulent factors of Gram-positive bacteria onto the cell wall. It has been shown that SrtA plays a pivotal role in the pathogenic processes of bacterial infection. Additionally, SrtA is not essential for microbial growth and viability, and its inhibition does not therefore place pressure on bacteria to develop drug-resistant mechanism. As an extracellular membrane enzyme, it can more readily be targeted by drugs relevant to intracellular enzymes. SrtA is thus an excellent target for the design and development of novel anti-virulence drugs against the drug-resistant Gram-positive bacteria that have become a major worldwide health problem. A number of SrtA inhibitors have so far been identified by techniques such as the rational design of substrate mimetic inhibitors based on the structure of the enzyme and enzyme substrates, identification of novel inhibitors among natural products, the discovery and development of SrtA inhibitors via high-throughput, and in silico screening of small molecule libraries followed by structural optimization. The present article reviews the progress made recently in the development of SrtA inhibitors as new antibacterial agents using similar techniques.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...