Efficient synthesis of biofuel precursor with long carbon chains from fructose†
Abstract
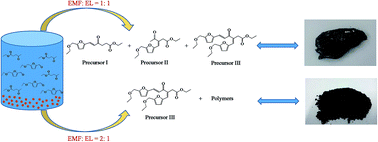
Long carbon biofuel precursors were efficiently synthesized via Aldol condensation of furans (furfural, 5-ethoxymethylfurfural, 5-hydroxymethylfural) and their derivatives (levulinic acid, ethyl levulinate) which were co-produced by fructose transformation in ethanol using acidic metal salt catalysts. High yields of furans and their derivatives were obtained and their mole ratios were adjusted. The effects of reaction time, temperature and water content on the mole ratios of furans and their derivatives were investigated in detail. The condensation reaction was conducted directly when the mole ratio of furans and their derivatives was located in the range of 1 to 2. The results showed that a total mole yield of furans and their derivatives as high as 91.6% could be obtained after fructose alcoholysis at 413 K for 2.0 h using Fe2(SO4)3 as a catalyst. After that, Aldol condensations of the produced furans and their derivatives with mole ratios of 1.9 and 1.1 were directly conducted using NaOH as the catalyst and 91.2% and 89.1% yields of precursors were gained, respectively. This technical route indicates a simple and feasible method to produce renewable long carbon biofuel from biomass.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...