A low temperature bottom-up approach for the synthesis of few layered graphene nanosheets via C–C bond formation using a modified Ullmann reaction†
Abstract
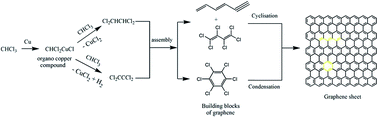
A low temperature, single-pot, bottom-up approach for the synthesis of few layered graphene sheets using the modified Ullmann reaction is reported. The synthesis protocol involved a solvothermal technique under an autogenic pressure of chloroform, which was used as the carbon source. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy revealed the formation of randomly aggregated, thin, crumpled graphene sheets with a thickness of ∼2 nm. Solid state 13C nuclear magnetic resonance and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy showed that the prepared graphene sheets have copious surface functionality. The possible growth mechanism for the formation of graphene sheets is proposed based on an analysis of the intermediate products by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectroscopy. The growth of few layered graphene sheets proceeded through addition and cyclization reactions of different chloroalkene intermediate products formed by the addition reaction of chloroform molecules, and not by the chain polymerization of chloroform molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...