Vacancy mediated ionic conduction in Dy substituted nanoceria: a structure–property correlation study
Abstract
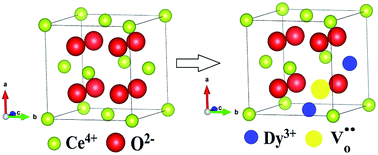
The oxygen vacancy evolution and ion dynamics in Dy doped nanoceria have been investigated with microstructural, optical and ionic conductivity studies. The influence of Dy3+ ions on the microstructures and the optical and ionic conductivity properties of these nanoparticles has been studied using X-ray diffraction, HR-TEM, EDAX, UV-vis, Raman and impedance spectroscopy. From Rietveld refinement of the XRD profiles, it has been found that the oxygen vacancies, lattice parameters and Ce–O bond lengths increase with Dy3+ ion concentration. The Rietveld analysis, together with HR-TEM, confirms the cubic fluorite structure with space group Fm![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) m of all the samples. The EDAX spectra show good stoichiometry of the different atoms in the samples. The direct band gap, calculated from UV-vis spectra, shows a red shift with increasing concentration of Dy3+ ions. Raman spectroscopy studies of the samples gave insight into their vibrational properties and pointed to the fact that the oxygen vacancy content increased significantly with the doping concentration. The number of oxygen vacancies and their interaction with dopant cations strongly influence the electrical properties of Dy doped ceria.
m of all the samples. The EDAX spectra show good stoichiometry of the different atoms in the samples. The direct band gap, calculated from UV-vis spectra, shows a red shift with increasing concentration of Dy3+ ions. Raman spectroscopy studies of the samples gave insight into their vibrational properties and pointed to the fact that the oxygen vacancy content increased significantly with the doping concentration. The number of oxygen vacancies and their interaction with dopant cations strongly influence the electrical properties of Dy doped ceria.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...