Fabrication, characterisation and in vitro biological activities of a sulfuretin-supplemented nanofibrous composite scaffold for tissue engineering
Abstract
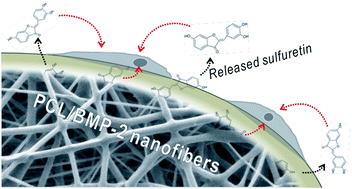
Electrospun micro/nanofibrous scaffolds are widely used in various tissue regeneration applications because they have a similar structure to the extracellular matrix and can induce high attachment, proliferation and even differentiation of cultured cells. Here, we designed a new composite scaffold consisting of poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL), bone morphogenetic protein (BMP-2) and sulfuretin fabricated using a combined process, i.e. electrospinning/plasma-treatment/coating. In the composite, we introduced a new bioactive component, sulfuretin, which was used as a cell stimulant to regenerate bone tissue. Sulfuretin release from the composite was controlled by coating of a fixed concentration of alginate. The in vitro biocompatibilities of the fibrous composites were examined using preosteoblasts (MC3T3-E1s), and the composite showed high cell adhesion and differentiation for a limited range of sulfuretin compared to the control, which lacked sulfuretin. These results suggest sulfuretin to be an effective supplemental bioactive agent for enhancing bone tissue growth on fibrous composite scaffolds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...