Shape-controlled synthesis of Pd nanoparticles for effective photocatalytic hydrogen production†
Abstract
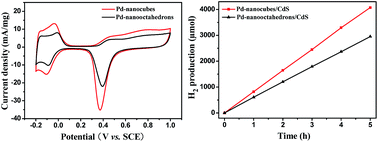
Pd nanocubes and nanooctahedrons were synthesized via shape-controlled technology and loaded onto a commercial CdS semiconductor photocatalyst for visible light photocatalytic hydrogen production via photooxidation of an aqueous ammonium sulfite solution. High resolution TEM analysis indicates that Pd nanooctahedrons (Pd NOTs) are enclosed by eight {111} facets, while synthesized Pd nanocubes (Pd NCs) are enclosed by six {100} crystal planes. The hydrogen evolution rate of Pd NC loaded CdS photocatalyst (Pd-NCs/CdS) is 1.38 times higher than that of Pd NOT loaded Pd-NOTs/CdS photocatalyst. The electrochemical characterization reveals that the higher photocatalytic activity of Pd-NCs/CdS is attributed to the higher electrochemical active surface area (ECSA) and the electrochemical activities of the Pd {100} crystal planes of Pd NCs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...