In situ chemical oxidative graft polymerization of aniline from phenylamine end-caped poly(ethylene glycol)-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes
Abstract
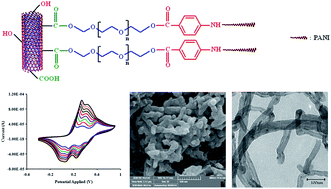
This paper describes the in situ chemical oxidative graft polymerization of aniline from phenylamine end-capped poly(ethylene glycol)-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). To this purpose, MWCNTs were carboxylated (MWCNTs-COOH) by conventional acid oxidation process, and then poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) chains were covalently attached to the carboxylated MWCNTs via a esterification reaction. The poly(ethylene glycol)-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs-PEG) was further reacted with p-anthranilic acid (4-aminobenzoic acid) to produce phenylamine end-caped poly(ethylene glycol)-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs-PEG-NH2). The graft polymerization of aniline monomers onto MWCNTs-PEG-NH2 was initiated by oxidized phenylamine groups after addition of ammonium peroxydisulfate (APS), and p-toluene sulfonic acid (p-TSA)-doped polyaniline was grown onto functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes via an oxidation polymerization method. The chemical structures of all samples as representatives were characterized by means of Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Moreover, electrical conductivity, electroactivity, optical properties, thermal behaviors, and morphologies of the synthesized samples were studied.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...