Highly sensitive detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP) based on lysozyme capped CdS quantum dots†
Abstract
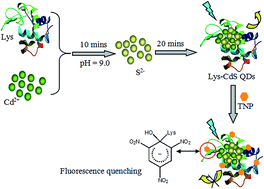
This work presents a novel method for nitroaromatic compound detection using lysozyme-capped CdS quantum dots (Lys-CdS QDs). Cd2+ can react with S2− to generate fluorescent CdS QDs in the presence of lysozyme. The Lys-CdS QDs can bind to 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP) in water via an acid–base pairing interaction between the electron-rich amino ligands and the electron-deficient aromatic ring of TNP. The electrons in the QDs transfer to the TNP molecules, leading to fluorescence quenching. The fluorescence decreases with an increase in TNP concentration and the fluorescence intensity is negatively proportional to the TNP concentration in the range from 0.5 μmol L−1 to 15 μmol L−1 with a detection limit of 0.1 μmol L−1. The newly-developed fluorescence probe shows excellent resistance to the interference of metal ions, such as Cu2+, Fe3+, and Pb2+, when compared with other fluorescence probes. The present method is cost-effective, convenient, and does not require any complicated synthetic procedures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...