In situ synthesis of natural rubber latex-supported gold nanoparticles for flexible SERS substrates†
Abstract
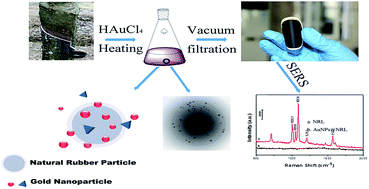
Natural rubber latex (NRL) from Hevea brasiliensis was used as a matrix to synthesize gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), leading to an organic–inorganic hybrid latex of NRL-supported AuNPs (AuNPs@NRL). The in situ and environmentally friendly preparation of AuNPs in an NRL matrix was developed by thermal treatment without using any other reducing agents or stabilizers because natural rubber particles and non-rubber components present in serum can serve as supporters for the synthesized AuNPs. As a result, the nanosized and well-dispersed AuNPs not only are decorated on the surface of natural rubber particles, but also can be found in the serum of NRL. The size of the AuNPs presented in NRL matrix can be controlled by adjusting the concentration of NRL. Furthermore, the flexible surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates made from the AuNPs@NRL through vacuum filtration presented good enhancement of the Raman probe molecule of 4-mercaptopyridine and outstanding SERS reproducibility. The capability of synthesizing the bio-supported nanohybrid latex provides a novel green and simple approach for the fabrication of flexible and effective SERS substrates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...