A microfluidic chip for high resolution Raman imaging of biological cells
Abstract
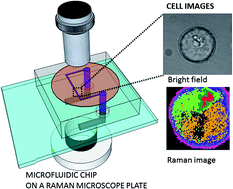
A microfluidic chip was designed, prepared and tested for integration with a confocal Raman imaging spectrometer with the specific purpose of enabling studies of individual biological cells. The design of the chip effectively overcomes the limitations arising from the high numerical aperture (NA) and short working distance objectives, which are necessary for high resolution imaging. The high confocal spatial resolution was achieved by a careful design of the geometry of the chip together with a thin, optically and Raman silent sealing window as the embedding medium for the channels. A leak-free microfluidic chip was obtained by surface plasma modification of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and optimization of the liquid loading parameters. Raman images of biological cells, which were transported by flow into the microfluidic chip, are presented as an example of a Raman-microfluidics application. The broad band Raman spectra from −50 cm−1 to 3650 cm−1 were recorded in 1600 frequency intervals without any signal enhancement or sample labeling. Raman images were recorded in ∼400 seconds and they typically consisted of 64 × 64 pixels with a step size of 250 nm, thus containing ∼4 × 106 data points altogether.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...