In vitro hyperthermia studied in a continuous manner using electric impedance sensing†
Abstract
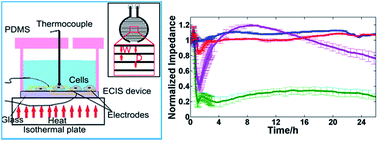
In this study, a new platform based on electric cell-substrate impedance sensing (ECIS) was constructed for the dynamic monitoring of changes in cells during and after hyperthermia treatments. ECIS profiling was compared with traditional methods for monitoring the status of A549 cells under three typical treatment conditions, i.e., 30 min of hyperthermia at 41, 43, and 45 °C. The impedance value rapidly changed, and severe morphological changes were observed during and after the hyperthermia. The impedance curves revealed that different hyperthermia conditions differentially affected the cells: the 41 °C treatment caused a minor decrease in impedance that almost completely recovered in 1–2 h; the 43 °C treatment led to a greater decrease in impedance, which also recovered over several hours before slowly decreasing again, possibly indicating apoptosis; the 45 °C treatment resulted in the greatest decrease in impedance, which never recovered, possibly indicating rapid necrosis. Further, these three hyperthermia treatment regimens were applied to four additional cell lines. By comparing the impedance curves of different cell lines, we found that cancer cells (HepG2) may be more sensitive to hyperthermia than normal cells (LO2). Moreover, different cancer cell lines (HeLa, MCF-7, A549, and HepG2) exhibited different thermal sensitivities. These results fit previous theories on hyperthermia, demonstrating that the platform established in this study is a useful analytical tool for the in vitro research of thermal therapy, and the dynamic data generated will enable us to examine phenomena and theories.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...