Performance in synthetic applications of a yeast surface display-based biocatalyst
Abstract
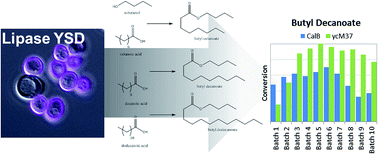
This work demonstrates the effectiveness of yeast surface display (YSD) as a scaffold for biocatalysts in hydrophobic, non-aqueous environments. Two lipases, Candida antarctica lipase B (CalB) and Photobacterium lipolyticum sp. M37 lipase (M37L), were immobilized independently by surface display on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The two YSD biocatalysts were employed to synthesize esters of butanol and saturated fatty acids of varying length (8 to 16 carbons) in heptane. Effects of fatty acid chain length and temperature on the esterification reaction were examined. The YSD catalysts synthesized butyl decanoate in 10 repeated batches with little loss in activity. Compared to a commercial immobilized lipase (Novozym 435), the activity of both YSD lipases was lower on a mass loading basis, but higher when normalized on estimates of protein loading. Initial-rate kinetics of the butyl decanoate reaction were measured for the CalB-displaying yeast. Kinetics and apparent activity of M37L in the multi-batch experiments depend heavily on water concentration; kinetics for M37L could not be elucidated with initial-rate methods. The difference between CalB and M37L in water requirements illustrates a critical parameter for optimization of lipase activity in non-aqueous environments. The activity of both lipases in a completely hydrophobic environment is a step towards more economical biocatalysis of industrial esterification.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...