Fe3+-induced oxidation and coordination cross-linking in catechol–chitosan hydrogels under acidic pH conditions
Abstract
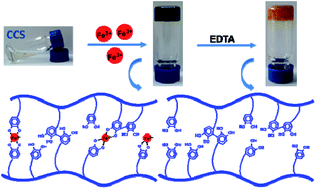
Mussel byssus is rich in Fe3+ and catechol-containing proteins; chemical interactions between these components vary widely with respect to changes in pH during byssal maturation. Previous studies have indicated the key role played by Fe3+–catechol interactions in regulating many attributes of biological materials, such as toughness, extensibility, and self-assembly. In this study, a platform based on a highly substituted catechol-modified chitosan (70%, CCS) was used to investigate the effect of pH on the reactions between Fe3+ and catechols. This study demonstrated that the Fe3+-induced CCS hydrogel is essentially a dual cross-linking system composed of covalent and coordination crosslinks, under acidic pH conditions. Variations in the Fe3+–catechol molar ratios could strongly affect the gelation time, physical properties, and UV-vis and Raman spectra. These changes represent different balance states between oxidation and coordination mechanisms in the hydrogel network. In addition, the system was subjected to optical microscopy and SEM in order to obtain a visual description of the dual-crosslinking mechanism.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...