Mesoporous silicas: improving the adsorption efficiency of phenolic compounds by the removal of amino group from functionalized silicas
Abstract
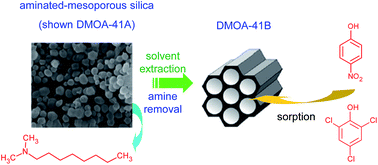
In this study, dimethyloctylamine-functionalized mesoporous silicas (MCM-41 and MCM-48 samples), which are designed to be anionic and cationic species sorbents, have been successfully deaminated by ethanolic extraction to obtain materials that would be able to remove neutral phenolic pollutants, namely, 4-nitrophenol and 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, from aqueous effluents. Solvent extraction was further applied to amine-functionalized MCM-41 and MCM-48 mesoporous materials with different chain lengths (N,N-dimethyldodecylamine, dodecylamine and hexadecylamine). The hexagonal mesoporous structure of MCM-41 and the three-dimensional cubic mesoporous structure of MCM-48 remain intact after dimethyloctylamine amination and template removal. The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of the different mesoporous materials are of type IV according to the IUPAC classification. The alcoholic extraction of the dimethyloctylamine moiety led to the formation of materials with a wide open pore structure, which are particularly suitable for the rapid adsorption of hydrophobic molecules. Isotherm data at ambient temperature were well fitted with the Langmuir model. Solvent extraction was further applied to the amine-functionalized MCM-41 and MCM-48 mesoporous materials with different chain lengths (N,N-dimethyldodecylamine, dodecylamine and hexadecylamine) and a statistical analysis of the sorption capacities vs. structural properties was performed. ANOVA Kruskal–Wallis tests showed that the adsorption of pollutants was not dependent on the type of mesoporous silicas (MCM-41 vs. MCM-48), rather it was dependent on the phenolic structure (PNP vs. TCP). A (weak linear) correlation between the pore size and sorption capacities could be established.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...