Effective heterogeneous electro-Fenton process of m-cresol with iron loaded actived carbon
Abstract
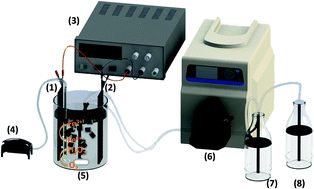
The degradation of m-cresol (MC) has been investigated by a heterogeneous electro-Fenton process using iron loaded activated carbon (Fe-AC) as the heterogeneous electro-Fenton catalyst. Experimental results demonstrated that MC was effectively removed through an electro-Fenton process. Calculated TOC removal and overall energy consumption showed that the use of a low iron concentration (28 mg L−1) increases the efficiency of the process. The reactions followed a pseudo-first order kinetic equation and kinetic coefficients confirm that the MC reduction, when it is alone, is faster than in the presence of a similar compound, tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ) (from 0.0935 to 0.0692 min−1); therefore TBHQ exerts an antioxidative protection effect. In all cases, it is concluded that heterogeneous electro-Fenton treatment with Fe-AC follows a two-step process: adsorption and oxidation; allowing removal rates higher than in the literature. In addition, the reusability of this catalyst was demonstrated by operating it in continuous mode. Finally, LC-MS analysis allowed the development of a plausible degradation route.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...