Porous graphene–carbon nanotube hybrid paper as a flexible nano-scaffold for polyaniline immobilization and application in all-solid-state supercapacitors†
Abstract
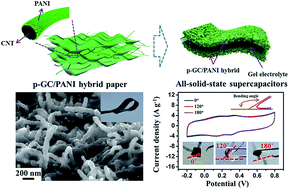
Polyaniline (PANI) has been recognized as an ideal candidate for electrode materials in supercapacitors. However, the relatively low electrical conductivity and poor cyclic stability severely limit its potential applications. Therefore, a proper substrate with carefully designed nanostructures for PANI immobilization is highly desirable for realizing its full performance. In this study, three-dimensional porous graphene–carbon nanotube (p-GC) hybrid papers with high porosity, excellent electrical conductivity and good flexibility were utilized as a nano-scaffold for the in situ polymerization of PANI, thus obtaining flexible p-GC/PANI ternary hybrid papers with hierarchical nanostructures. The good electrical conductivity and optimized porous nanostructure of the p-GC hybrid paper provides improved conductive pathways and high surface area, ensuring the efficient utilization of the pseudocapacitance of PANI. Thus, the ternary hybrid paper exhibits a high specific capacitance of up to 409 F g−1 at a current density of 10 A g−1, as well as excellent rate and cyclic performance. Furthermore, the dimensional confinement of PANI particles within the p-GC framework effectively prohibits volume expansion and shrinkage upon electrolyte soakage and cycling. Therefore, the p-GC hybrid paper with tunable hierarchical nanostructures can act as a promising substrate to enhance the electrochemical properties of PANI or other electroactive materials and can be easily extended to the design of next-generation high-performance flexible supercapacitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...