Cathodic and anodic photocurrents generation from melem and its derivatives†
Abstract
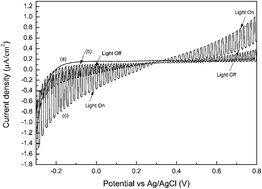
Melem and its derivatives were synthesized from melamine by a two-step heat treatment method between 400 and 650 °C in air. It was demonstrated that such polymeric C–N semiconductors possess a photoelectrochemical (PEC) conversion effect with both photocathodic and photoanodic characteristics, which was proposed to be caused by the formation of tri-s-triazine ring. The dimelem synthesized at 450 °C exhibited the highest PEC conversion activity. The possible reasons were discussed. The unique bidirectional photocurrent generation makes melem and its derivatives attractive photoelectrochemical materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...