Fabrication of a photo-catalytic cell using polymer-based composite films and investigation of its performance in the degradation of methyl blue
Abstract
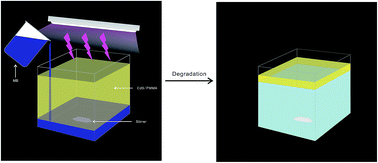
A facile method for the preparation of flexible semiconductor/polymer composite films with a CdS and ZnS particle layer on their surface has been developed. The as-prepared composite films were used as building blocks to fabricate a photo-catalytic cell. Methyl methacrylate (MMA) and butyl methacrylate (BMA) were copolymerized via free radical polymerization. BMA was used to tune the flexibility of the films. Allyl methyl sulfide (AMS) and N-allylmethylamine (AMA) were used as functional monomers to coordinate with Cd2+/Zn2+ ions. Cd2+/Zn2+ ions were chemically bonded to the PMMA-BMA-AMS (PMBS) or PMMA-BMA-AMA (PMBA) films. By addition of a thioacetamide (TAA) solution, S2− ions were gradually released and combined with Cd2+/Zn2+ ions to form CdS/ZnS particles. Accordingly, CdS/PMBA, ZnS/PMBA, CdS/PMBS and ZnS/PMBS films were prepared. The composite films were characterized and used to fabricate a photo-catalytic cell. The well-designed cell showed excellent performance in the degradation of the pollutant methyl blue (MB). Also, this cell could be used repeatedly just by rinsing with water after use.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...