Antibacterial hybrid cellulose–graphene oxide nanocomposite immobilized with silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
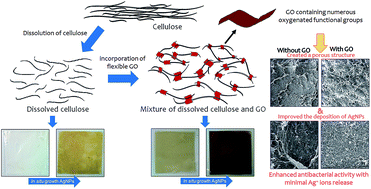
A hybrid nanocomposite cellulose membrane containing graphene oxide and silver nanoparticles was produced via a two step synthesis method. First, regenerated cellulose membranes containing different percentages of graphene oxide (GO) were produced by coagulating the mixture in an acid coagulating bath. Afterward, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were in situ synthesized onto the membranes using the modified Tollens' method. The presence of GO on the cellulose membranes significantly enhanced the deposition of AgNPs due to the electrostatic interaction between the positively charged silver ammonia complex and negatively charged oxygenated functional groups of GO before the reduction to AgNPs. The AgNPs content of the membrane with 1 wt% of GO was approximately 26 times greater than that of the neat cellulose membrane. More interestingly, the presence of GO significantly lowered the release of Ag ions and leaching of AgNPs into the aqueous solution. The produced composite membranes exhibited strong antibacterial activity against S. aureus and E. coli.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...