Fabrication of hydroxyapatite/chitosan porous materials for Pb(ii) removal from aqueous solution
Abstract
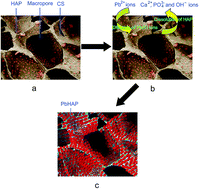
Lead is one of the common heavy metal contaminants that pose a significant threat to human health. Herein, a freeze-drying method has been used to fabricate hydroxyapatite/chitosan (HAP/CS) porous materials for the removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions. The HAP/CS porous materials possessed interconnected three-dimensional macropores with pore sizes of 100–300 μm. Low-crystallinity HAP particles were dispersed uniformly among the porous materials. Adsorption experiments for Pb(II) ions were conducted under flow conditions. The adsorption capacity of the HAP/CS porous material was found to be 264.42 mg g−1, while that of the CS porous material was only 5.67 mg g−1. The better adsorption property of the HAP/CS porous material than the CS porous material was attributed to the presence of HAP particles in the composite material. During the adsorption process, the HAP particles were converted to rod-like lead hydroxyapatite (PbHAP, Pb10(PO4)6(OH)2) particles via a dissolution–precipitation reaction. Adsorption kinetic studies revealed that the adsorption of Pb(II) ions on the HAP/CS porous material exhibited a good fit to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. Therefore, the HAP/CS porous materials possess a great potential for the removal of Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...