Stabilization of silicon nanoparticles in graphene aerogel framework for lithium ion storage†
Abstract
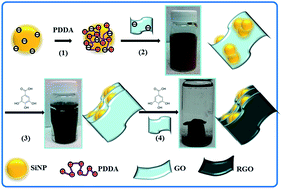
The severe volume change and aggregation of silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) when used as an anode for lithium ion batteries (LIBs) are the key issue. Here, we demonstrate a novel approach to wrapping SiNPs in three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide (RGO) aerogel. The RGO aerogel not only provides a porous network for entrapping SiNPs to accommodate the volume change during cycling, but also facilitates electrolyte transport. Furthermore, the continuous RGO network is favourable for electron transfer. The graphene-wrapped SiNPs were stable and displayed an excellent rate capacity, delivering a reversible capacity of about 2000 mA h g−1 after 40 cycles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...