Understanding the cation specific effects on the aqueous solubility of amino acids: from mono to polyvalent cations†
Abstract
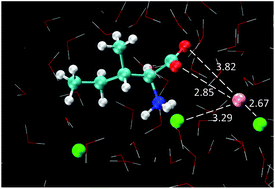
The interactions established by mono and polyvalent cations in natural media have important implications on the structure formation, function and physico-chemical behavior of biomolecules, playing therefore a critical role in biochemical processes. In order to further elucidate the molecular phenomena behind the cation specific effects in biological environments, and clarify the influence of the charge of the ions, solubility measurements and molecular dynamics simulations were performed for aqueous solutions of three amino acids (alanine, valine and isoleucine), in the presence of a series of inorganic salts comprising mono-, di- and trivalent cations (LiCl, Li2SO4, K2SO4, CaCl2, AlCl3 and Al2(SO4)3). The evidence gathered indicates that the mechanism by which (salting-in inducing) polyvalent cations affect the solubility of amino acids in aqueous solutions is different from that of monovalent cations. A consistent and refined molecular description of the effect of the cation on the solubility of amino acids based on specific interactions of the cations with the negatively charged moieties of the biomolecules is here proposed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...