Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel C3-functionalized oxindoles as potential Pim-1 kinase inhibitors
Abstract
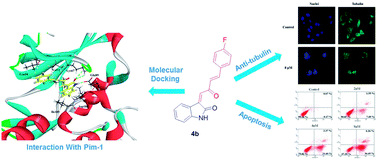
A novel series of C3-functionalized oxindoles, 3-(2-oxo-4-phenylbut-3-en-1-ylidene)indolin-2-ones, were designed, synthesized and investigated for inhibition of cell proliferation against different types of human cancer cell lines, including SW620, HeLa and A549. This biological study showed that these compounds containing the scaffolds of indole and aromatic α,β-unsaturated ketone had moderate to significant antitumor activities. Further study suggested that compound 4b, as one of this kind of structure derivative, showed broad-spectrum antitumor activities against MCF-7, PC-3, SKOV-3, U87, SMMC-7721, SY5Y and A875 cancer cell lines. Besides, the results of the inhibition of Pim kinases indicated that compound 4b showed selective and efficient anti-Pim-1 kinase activity (IC50 = 5 μM). Docking simulation, flow cytometry (FCM), and Hoechst 33342 staining assay suggested that the most active compound 4b induced cell death through apoptosis via binding to the active ATP pocket of Pim-1. Moreover, it showed that compound 4b had strong inhibition of tubulin polymerization which may be caused by inhibiting Pim-1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...