Ionisation of methyl iodide clusters using nanosecond laser pulses: detection of multiply charged positive ions, negative ions and energetic electrons
Abstract
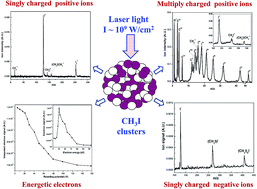
Methyl iodide clusters have been ionised using laser pulses of intensity ∼109 W cm−2 at 266, 355, 532 and 1064 nm and the ions produced in the laser–cluster interaction were analysed with a time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Multiply charged atomic ions of carbon and iodine have been observed at 355, 532 and 1064 nm. The charge state of the multiply charged atomic ions was found to enhance at longer laser wavelengths with the highest charge state of I10+ observed at 1064 nm. The charge density produced upon interaction with the clusters was also measured at different laser wavelengths. The charge density was found to increase with laser wavelength which complements the time-of-flight mass spectra results. The generation of negative ions like I−, (CH3I)I−, (CH3I)2I− were also observed in the mass spectra. In order to understand the ionisation mechanism of methyl iodide clusters at a gigawatt intense laser field, the kinetic energy of the electrons produced upon laser–cluster interaction was measured at different laser wavelengths. At 266 and 355 nm, an electron signal could not be observed because of low yield. However, at 532 and 1064 nm, electrons with kinetic energy up to ∼50 & ∼100 eV were observed having a mean electron energy of ∼5 & ∼25 eV respectively. Based on the electron energy measurement, the generation of multiply charged atomic ions can be explained using an electron heating mechanism at a gigawatt laser field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...