Ni cluster nucleation and growth on the anatase TiO2(101) surface: a density functional theory study†
Abstract
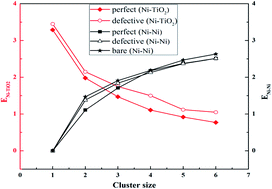
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations are carried out to study the nucleation and growth rule of Ni clusters on both a perfect and defective anatase TiO2(101) surface using supported Nin (n = 1–6) cluster models. Our results show that a single Ni atom prefers to adsorb at the bridge site formed by two-coordinated oxygen (2cO) atoms on the perfect TiO2(101) surface and at the 3cO-bridge site on the defective TiO2(101) surface. The active site for Ni cluster growth on the perfect TiO2(101) surface shifts from the bridge site of two 2cO atoms or the 2cO–6cTi–3cO bridge site for Ni1, Ni2, and Ni3 clusters to the 2cO–5cTi bridge site for Ni4, Ni5, and Ni6. The Ni cluster cohesive energy remains constant with cluster size variation on both the perfect and defective surface. The Ni–TiO2 interaction is the main driving force of the initial Ni nucleation stage, and the Ni–Ni interaction begins to control the Nin cluster growth process with increased cluster size.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...