The influence of pH and temperature on the stability of flutamide. An HPLC investigation and identification of the degradation product by EI+-MS
Abstract
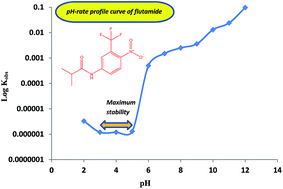
The chemical stability of flutamide (FLT) was investigated using a new validated stability-indicating HPLC method. Separation of FLT from its degradation product was achieved on a C18 column using a mobile phase of methanol–phosphate buffer (0.04 M, pH 4.0) (75 : 25, v/v) with UV-detection at 240 nm. The method exhibited excellent linearity for FLT over the concentration range of 0.2–25.0 μg mL−1. FLT was found to be labile to degradation in buffered, acidic and alkaline solutions. The degradation kinetics of FLT in aqueous solutions was evaluated as a function of pH and temperature. Degradation of FLT followed first-order kinetics and Arrhenius behavior over the temperature ranges of 70–100 and 60–90 °C under acidic and alkaline conditions, respectively. The pH-rate profile was studied over the pH range of 2.0–12.0 with a maximum stability at pH 3.0–5.0. The activation energies for hydrolysis of FLT were calculated as 79.4 and 52.0 kJ mol−1 at pH 0.5 (0.3 M HCl) and 12.5 (0.03 M NaOH), respectively. 4-Nitro-3-trifluoromethyl aniline was identified by mass spectrometry to be the degradation product resulting from the hydrolysis of FLT. The proposed HPLC method was validated according to ICH guidelines and applied for the quality control of FLT in commercial tablets with a mean percentage recovery of 100.09 ± 0.20%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...