Relationship between screw structure and properties of recycled glass fiber reinforced flame retardant nylon 46
Abstract
Considering environmental protection and economic requirements, the use of recycled glass fiber reinforced flame retardant nylon 46 (RGFFRPA46) is of significant importance. In this work, the mechanical, thermal, rheological and flame retardant properties of the recycled RGFFRPA46 were evaluated by varying shear screws. To establish the relationship between the screw structure and the properties of RGFFRPA46, the carboxyl content (CC) and viscosity-average molecular weight (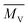 ) of PA46, the distribution and average length of glass fiber (
) of PA46, the distribution and average length of glass fiber (![[L with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_004c_0304.gif) ) and microscopic appearance of RGFFRPA46 were investigated. The results showed that the shear force resistance time of RGFFRPA46 increased with the increase of the shear strain and with the ratio of length to diameter of the used extruder. As a result,
) and microscopic appearance of RGFFRPA46 were investigated. The results showed that the shear force resistance time of RGFFRPA46 increased with the increase of the shear strain and with the ratio of length to diameter of the used extruder. As a result, 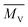 of PA46,
of PA46, ![[L with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_004c_0304.gif) and the percentage of glass fiber length (Vj), which was higher than critical length, decreased, whereas the CC of PA46 increased significantly. The mechanical and rheological properties were sensitive to these variations, particularly the decrease in impact, tensile, flexural strength and shear viscosity of RGFFRPA46. Furthermore, the influence of degradation on
and the percentage of glass fiber length (Vj), which was higher than critical length, decreased, whereas the CC of PA46 increased significantly. The mechanical and rheological properties were sensitive to these variations, particularly the decrease in impact, tensile, flexural strength and shear viscosity of RGFFRPA46. Furthermore, the influence of degradation on 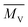 of PA46 and
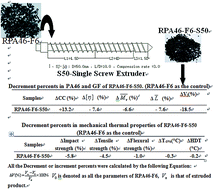
of PA46 and ![[L with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_004c_0304.gif) were negative to the thermal properties of RGFFRPA46 after extrusion. However, the flame retardant properties of RGFFRPA46 were independent of the degradation. All of them achieved a UL-94 V-0 classification, and passed the glow wire ignition temperature (775 °C) test along with LOI of 36.7%. When RGFFRPA46 was extruded by a single screw extruder with the lowest shear force, a decrease of only 5.8% was observed in mechanical properties with negligible reductions in thermal and flame retardant properties.
were negative to the thermal properties of RGFFRPA46 after extrusion. However, the flame retardant properties of RGFFRPA46 were independent of the degradation. All of them achieved a UL-94 V-0 classification, and passed the glow wire ignition temperature (775 °C) test along with LOI of 36.7%. When RGFFRPA46 was extruded by a single screw extruder with the lowest shear force, a decrease of only 5.8% was observed in mechanical properties with negligible reductions in thermal and flame retardant properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...