A facile method to enhance ferroelectric properties in PVDF nanocomposites
Abstract
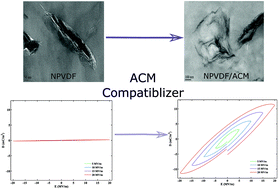
Poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/nanoclay composites were prepared using melt compounding. The effect of acrylic rubber (ACM) as a compatibilizer on different polymorph formation and on the ferroelectric properties of nanocomposites were investigated. The intercalation and morphological structure of the samples were studied using X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The infrared spectroscopy and X-ray analysis revealed the coexistence of β and γ crystalline forms in PVDF–clay nanocomposite, while in partially miscible PVDF/ACM/clay hybrids, three polymorphs of α, β and γ coexisted. The coefficients of electric field–polarization (E–P) Taylor expansion were calculated based on the Lorentz theory. Using a genetic algorithm, complex dielectric susceptibilities as well as the dielectric constants for each sample were calculated and optimized. The predicted dielectric constants were found to be in good agreement with the experimental results. A dielectric constant of 16 (10 Hz) was obtained for PVDF/ACM/clay (90/10/5), which was 40% higher than that of the PVDF–clay (100/5) nanocomposite without ACM. The improved dielectric performance of the nanocomposites can be attributed to the compatibilizing effect of ACM, which facilitated the growth of β polymorph in the sample.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...