In situ formation of gold/silver bi-metal nanodots on silica spheres and evaluation of their microbicidal properties†
Abstract
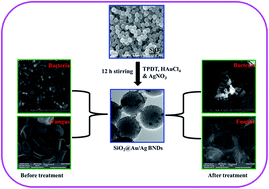
An environmentally benign synthetic method of seedless and one-step growth of 2–4 nm sized gold/silver (Au/Ag) bi-metal nanodots (BNDs) on preformed amine functionalized silica (SiO2) spheres via co-reduction of metal precursors at room temperature and their antimicrobial activity are reported. The resulting BNDs on SiO2 spheres (SiO2@/Au/Ag) exhibited a distinctive surface plasmon resonance (SPR) band between the Ag and Au nanoparticle (NP) SPR absorption regions. The deposition of BNDs on SiO2 spheres was confirmed from the high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analyses. The SiO2@Au/Ag BNDs with different concentrations of Au and Ag (SiO2@Au25/Ag75, SiO2@Au50/Ag50 and SiO2@Au75/Ag25 BNDs) exhibited a broad-spectrum of antimicrobial activities involving significant growth inhibition of Gram negative bacterial strains (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa), a Gram positive bacterial strain (Bacillus thuringiensis) and a fungal strain (Trichoderma longibrachiyatum MKU-1). The mechanism of interaction between the BNDs and microbial strains was analyzed through scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results confirmed that the treated microbial cells were damaged and have pits on the cell surface. The results evidently demonstrated the antimicrobial activity of the SiO2@Au/Ag BNDs even at lower concentrations of Ag (SiO2@Au75/Ag25), which may be suitable for the formation of potential microbicidal materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...