A novel coumarin derivative as a sensitive probe for tracing intracellular pH changes†
Abstract
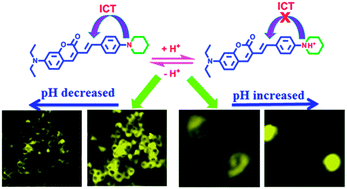
A new pH sensitive probe, 7-diethylamino-3-[2-(4-piperidin-1-yl-phenyl)-vinyl]-chromen-2-one (CS-P), was designed and synthesized. This probe was constructed by introduction of piperidine to the coumarin stem. It exhibited high pH sensitivity ranging from pH 5.9 to pH 3.0 (pKa = 4.55), and in vitro cell imaging showed that its fluorescence intensity was distinctly related to the cellular pH changes induced by chloroquine or dexamethasone. Demonstrated as having good cell membrane permeability and high pH sensitivity, this probe is suitable for tracing the intracellular pH changes from neutral to acidic conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...