Classical photopolymerization kinetics, exceptional gelation, and improved diffraction efficiency and driving voltage in scaffolding morphological H-PDLCs afforded using a photoinitibitor
Abstract
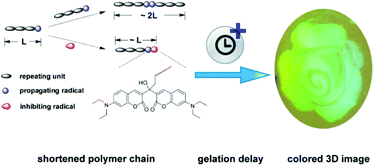
Holographic polymer dispersed liquid crystals (H-PDLCs) pertain to one type of intriguing switchable electro-optical device, and there is a constant need to quantitatively understand the photopolymerization kinetics and gelation process during the formation of H-PDLCs for the purpose of improving the diffraction efficiency and driving voltage. Herein, we quantitatively investigate the effect of the photoinitibitor composed of 3,3′-carbonylbis(7-diethylaminocoumarin) (KCD) and N-phenylglycine (NPG), with initiation and inhibition functions simultaneously generated under monochromatic illumination, on the formation of H-PDLCs. The outcomes reveal that an augmentation of KCD loading from 0.3 × 10−3 to 1.4 × 10−3 mol L−1 dramatically promotes the photopolymerization rate and monomer conversion. Reversely, a further increase in KCD content drastically depresses photopolymerization. The numerical deduction shows that the kinetics complies with the classical photopolymerization kinetics characteristics in the full range of the KCD content. Counterintuitively, the gelation time almost keeps constant when the KCD content is less than 1.8 × 10−3 mol L−1, and then is able to grow by more than 4 times when the KCD loading further increases. Ketyl radical inhibition, which subsequently results in shortened weight-average chain lengths and increased gel point conversions, is believed to account for the kinetics and exceptional gelation behaviors. H-PDLCs with a scaffolding morphology are formed, and with an augmentation of the KCD content, the segregation degree and diffraction efficiency significantly improve from zero to 64% and 78 ± 11%, respectively, and then level off, allowing for the facile fabrication of glass-free colored 3D images; while the critical driving voltage gradually decreases from 8.9 ± 1.0 to 4.6 ± 0.7 V μm−1.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...