Double pH-responsive supramolecular copolymer micelles based on the complementary multiple hydrogen bonds of nucleobases and acetalated dextran for drug delivery†
Abstract
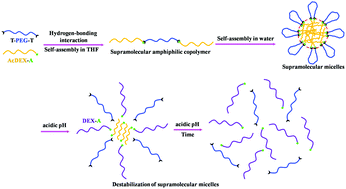
A double pH-responsive supramolecular copolymer micelle was successfully developed, which was based on complementary multiple hydrogen bonds of nucleobases and acetalated dextran. The thymine-terminated poly(ethylene glycol) (T-PEG-T) and adenine-terminated acetalated dextran (AcDEX-A) were synthesized and used to construct supramolecular amphiphilic triblock copolymer AcDEX-A:T-PEG-T:A-AcDEX, which could be further self-assembled into supramolecular micelles in water. These micelles were stable at pH 7.4, but disruptive at pH 5.0 due to the double pH-sensitivity of hydrogen bonds within the copolymer backbones and the hydrolysis of the acetalated dextran. The hydroxyl coverage of Ac-DEX had an important effect on the critical micelle concentration (CMC) and particle size of AcDEX-A:T-PEG-T:A-AcDEX micelles, which were observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). In addition, turbidometry was utilized to evaluate the effect of pH-responsivity of AcDEX-A:T-PEG-T:A-AcDEX micelles and these supramolecular micelles were completely decomposed at pH 5.0. Cytotoxicity evaluation showed good biocompatibility of these micelles, and doxorubicin (DOX) was encapsulated into supramolecular micelles as a model drug. The in vitro drug release profile showed that the DOX release speed at pH 5.0 could be adjusted by changing the hydroxyl coverage of Ac-DEX. Meanwhile, DOX-loaded supramolecular micelles could be efficiently internalized into cancer cells and showed similar inhibition of proliferation of the Hela cell as free DOX. This work provided a new method for enabling a rapid intracellular release of drugs by using double pH-sensitive hydrogen bonds and acetalated dextran, which would have the potential to be applied in controlled drug delivery.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...