Hyperactive Arg39Lys mutated mnemiopsin: implication of positively charged residue in chromophore binding cavity†
Abstract
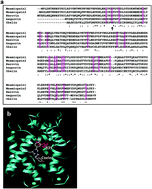
Mnemiopsin, a Ca2+-regulated photoprotein isolated from Mnemiopsis leidyi, belongs to the family of ctenophore photoproteins. These proteins emit blue light from a chromophore, which is tightly but non-covalently bound in their central hydrophobic core that contains 21 conserved residues. In an effort to investigate the role of Arg39 (the sole charged residue in coelenterazine binding cavity of ctenophore photoproteins) in bioluminescence properties of these photoproteins, three mutated forms of mnemiopsin 1 (R39E, R39K and R39M) were constructed and characterized. The results indicate that while the luminescence activity of R39K mutated mnemiopsin has increased about nine fold compared to the wild type, R39M and R39E mutated mnemiopsins have entirely lost their activities. The most distinguished properties of R39K mutated photoprotein are its high activity, slow rate of luminescence decay and broad pH profile compared to the wild type. The complete loss of bioluminescence activity in mutated photoproteins with negatively charged and aliphatic residues (R39E and R39M, respectively) shows that the presence of a positively charged residue at this position is necessary. The results of spectroscopic studies, including CD, intrinsic and extrinsic fluorescence measurements and acrylamide quenching studies show that, while the substitutions lead to structural rigidity in R39E and R39M mutated mnemiopsins, structural flexibility is obvious in R39K mutated mnemiopsin. The presence of a more localized positive charge on ε-amino group of Lys compared to guanidinium group of Arg residue in close proximity to the choromophre might affect its fixation in the binding cavity and result in increased bioluminescence activity in this mutated photoprotein. It appears that the polarity and flexibility of positively charged residue at this position finely tunes the luminescence properties of ctenophore photoproteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...