Synthesis and antibiotic activity of oxazolidinone–catechol conjugates against Pseudomonas aeruginosa†
Abstract
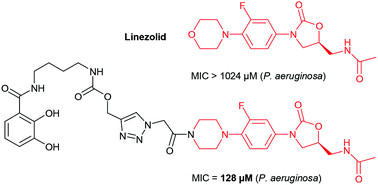
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a Gram-negative pathogenic bacterium responsible for severe infections in which resistance to most of the approved families of antibiotics is increasing. Oxazolidinone antibiotics are active against many Gram-positive bacteria, but are only weakly active against Gram-negative pathogens. We describe the synthesis of conjugates between a catechol moiety and oxazolidinone antibiotics. These conjugates were significantly more active against P. aeruginosa (218–1024 μM) than linezolid (MIC > 1024 μM), the reference molecule from the oxazolidinone family. Antibiotic activity was slightly higher in medium depleted of iron, suggesting the involvement of a bacterial iron uptake system in this biological activity. The bacterial iron uptake pathway involved in the transport is still to be addressed, but the present data excluded a contribution of the enterobactin transporter PfeA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...