On the interaction between the imidazolium cation and aromatic amino acids. A computational study†
Abstract
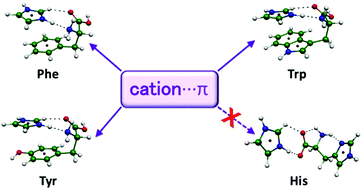
Complexes formed by the imidazolium cation and the aromatic amino acids, phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan, and histidine have been studied by using computational methods. Complexation energies estimated at the MP2.X level amount to −123.3, −124.6, −131.5 and −145.5 kJ mol−1 for Phe, Tyr, Trp and His, respectively. The results obtained for Phe, Tyr and Trp complexes are similar, with the most stable minima corresponding to structures with the imidazolium cation stacked over the rings. The cation forms hydrogen bonds with the amino acid while establishing cation⋯π contacts with the aromatic rings. Extended structures with the amino acids in zwitterionic form are almost equally stable, though. The interaction is controlled by electrostatics and induction, though the preference for the stacked minima is due to larger contributions from induction and dispersion despite the energy cost of folding the amino acid. His complexes exhibit a totally different behaviour, and no structures displaying cation⋯π interactions are found among the most stable minima. Most favourable complexes of His show the cation hydrogen bonded to the amino acid in extended zwitterionic form. Overall, Phe, Tyr and Trp complexes can show parallel structures in competition with similarly stable zwitterionic ones, while His only shows zwitterionic minima, with a stability even larger than any of the other aromatic amino acids, though lacking participation of the π cloud in the interaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...