Expanding the scope of N → S acyl transfer in native peptide sequences†
Abstract
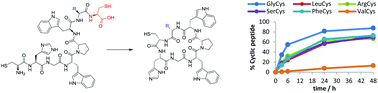
Understanding the factors that influence N → S acyl transfer in native peptide sequences, and discovery of new reagents that facilitate it, will be key to expanding its scope and applicability. Here, through a study of short model peptides in thioester formation and cyclisation reactions, we demonstrate that a wider variety of Xaa-Cys motifs than originally envisaged are capable of undergoing efficient N → S acyl transfer. We present data for the relative rates of thioester formation and cyclisation for a representative set of amino acids, and show how this expanded scope can be applied to the production of the natural protease inhibitor Sunflower Trypsin Inhibitor-1 (SFTI-1).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...