Locked nucleic acid (LNA) induced effect on the hybridization and fluorescence properties of oligodeoxyribonucleotides modified with nucleobase-functionalized DNA monomers†
Abstract
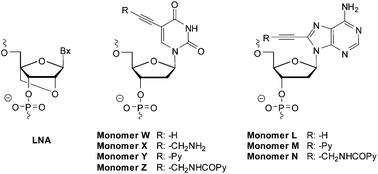
LNA and nucleobase-modified DNA monomers are two types of building blocks that are used extensively in oligonucleotide chemistry. However, there are only very few reports in which these two monomer families are used alongside each other. In the present study we set out to characterize the biophysical properties of oligodeoxyribonucleotides in which C5-modified 2′-deoxyuridine or C8-modified 2′-deoxyadenosine monomers are flanked by LNA nucleotides. We hypothesized that the LNA monomers would alter the sugar rings of the modified DNA monomers toward more RNA-like North-type conformations for maximal DNA/RNA affinity and specificity. Indeed, the incorporation of LNA monomers almost invariably results in increased target affinity and specificity relative to the corresponding LNA-free ONs, but the magnitude of the stabilization varies greatly. Introduction of LNA nucleotides as direct neighbors into C5-pyrene-functionalized pyrimidine DNA monomers yields oligonucleotide probes with more desirable photophysical properties as compared to the corresponding LNA-free probes, including more intense fluorescence emission upon target binding and improved discrimination of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). These hybrid oligonucleotides are therefore promising probes for diagnostic applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...