1,5-Benzodiazepine derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents: design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and structure–activity relationships†
Abstract
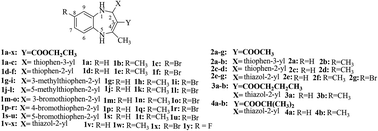
36 Novel 1,5-benzodiazepine derivatives were rationally designed and synthesized according to the principle of superposition of bioactive substructures by the combination of 1,5-benzodiazepines, thiophene or thiazole and ester group. The structures of the target compounds have been characterized by IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, MS and elemental analysis. The structure of 1v was further determined using X-ray single crystal diffraction. All synthesized 1,5-benzodiazepine derivatives were evaluated for their in vitro antimicrobial activity against C. neoformans, C. neoformans clinical isolates, C. albicans, E. coli and S. aureus. The bioactive assay results revealed that most of the 1,5-benzodiazepine derivatives exhibited considerable potency against all of the tested strains. In particular, compounds 1v and 1w (MIC: 2–6 μg mL−1, MFC: 10–14 μg mL−1) exhibited excellent antifungal activity and were found to be 32–64 and 9–12.8 times more potent than the reference drugs against C. neoformans, respectively. Moreover, compound 1v (MIC: 40 μg mL−1) displayed equipotent antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus compared to the reference drugs. The most potent of the synthesized compounds 1v and 1w were further studied by evaluating their cytotoxicities, and the results showed that they had relatively low level cytotoxicity for BV2 cell. A preliminary study of the structure–activity relationship revealed that substituents in the phenyl ring and the thiophene ring had a great effect on the antimicrobial activity of these compounds. In addition, the thiazole ring at C2 may be a pharmacophore of these compounds and COOC2H5 group at C3 is the best substituent for the maintenance of antimicrobial activities at low concentrations (1.5625 μg per disc).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...