Base-modified NAD and AMP derivatives and their activity against bacterial DNA ligases†
Abstract
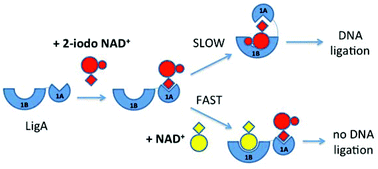
We report the chemical synthesis and conformational analysis of a collection of 2-, 6- and 8-substituted derivatives of β-NAD+ and AMP, and their biochemical evaluation against NAD+-dependent DNA ligases from Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Bacterial DNA ligases are validated anti-microbial targets, and new strategies for their inhibition are therefore of considerable scientific and practical interest. Our study includes several pairs of β-NAD+ and AMP derivatives with the same substitution pattern at the adenine base. This has enabled the first direct comparison of co-substrate and inhibitor behaviour against bacterial DNA ligases. Our results suggest that an additional substituent in position 6 or 8 of the adenine base in β-NAD+ is detrimental for activity as either co-substrate or inhibitor. In contrast, substituents in position 2 are not only tolerated, but appear to give rise to a new mode of inhibition, which targets the conformational changes these DNA ligases undergo during catalysis. Using a molecular modelling approach, we highlight that these findings have important implications for our understanding of ligase mechanism and inhibition, and may provide a promising starting point for the rational design of a new class of inhibitors against NAD+-dependent DNA ligases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...