Rapid probing of sialylated glycoproteins in vitro and in vivo via metabolic oligosaccharide engineering of a minimal cyclopropene reporter†
Abstract
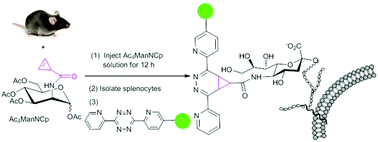
ManNAc analogues are important chemical tools for probing sialylation dynamically via metabolic oligosaccharide engineering (MOE). The size of N-acyl and the nature of the chemical handle are two determinants of metabolic incorporation efficiency. We demonstrated a minimal, stable, bioorthogonal, and reactive N-Cp (N-(cycloprop-2-ene-1-ylcarbonyl)) group and the imaging of sialylated glycans using Ac4ManNCp in vitro and in vivo. The results revealed that the Cp group can efficiently be incorporated into the cellular sialic acid and detected rapidly by the reaction with FITC-Tz in different cells. The metabolic incorporation efficiency of non-cytotoxic Ac4ManNCp is not only superior to Ac4ManNMCp, but also superior to the widely-used Ac4ManNAz in some cell lines. Moreover, when Ac4ManNCp was administered to mice, a rapid and intense labelling of splenocytes as well as glycoproteins of sera and organs was observed. This is the first reported metabolic labelling of cyclopropene-modified sugars in vivo. Therefore, Ac4ManNCp is a powerful probe for efficient and rapid MOE and it may find wide applications in the labelling of glycans.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...